
Do you take biotin for hair growth? What about vitamin B7, coenzyme R or vitamin H?
These are just different names for a very common vitamin that many naturals take for hair growth called biotin. The real question is does taking biotin for hair growth really work?
Let’s dive a little deeper.
Table of Contents
- 1 Is Biotin Good for Curly Hair Growth?
- 2 What Is Biotin?
- 3 Sources: Food High in Vitamin B7
- 4 Using Biotin for Healthy Hair Growth: The Reason People Are Taking Biotin Supplements
- 5 Did You Know That Biotin Deficiencies Are Very Rare?
- 6 Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology
- 7 How Much Vitamin B7 Should You Take?
- 8 Should You Worry About Toxicity with Vitamin B7?
- 9 The Best Hair Vitamins (Other Than Biotin) for Faster Hair Growth
- 10 Are Hair Growth Vitamins and Supplements Safe?
Is Biotin Good for Curly Hair Growth?
Yes, biotin is good for curly hair growth. Biotin is a water-soluble B-complex vitamin that is required for the health of curly hair. Biotin intake plays an important part in preventing hair loss and encouraging natural hair growth. Although, biotin supplements may not be necessary because biotin deficiencies are rare.
What Is Biotin?
There are many names for biotin, including coenzyme R, vitamin B7, and vitamin H.
In simple terms, vitamin B7 is a water-soluble B-complex vitamin that is often found in foods. Biotin is required by the human body for cell growth, producing fatty acids and it's also essential for the metabolism of amino acids and fats.
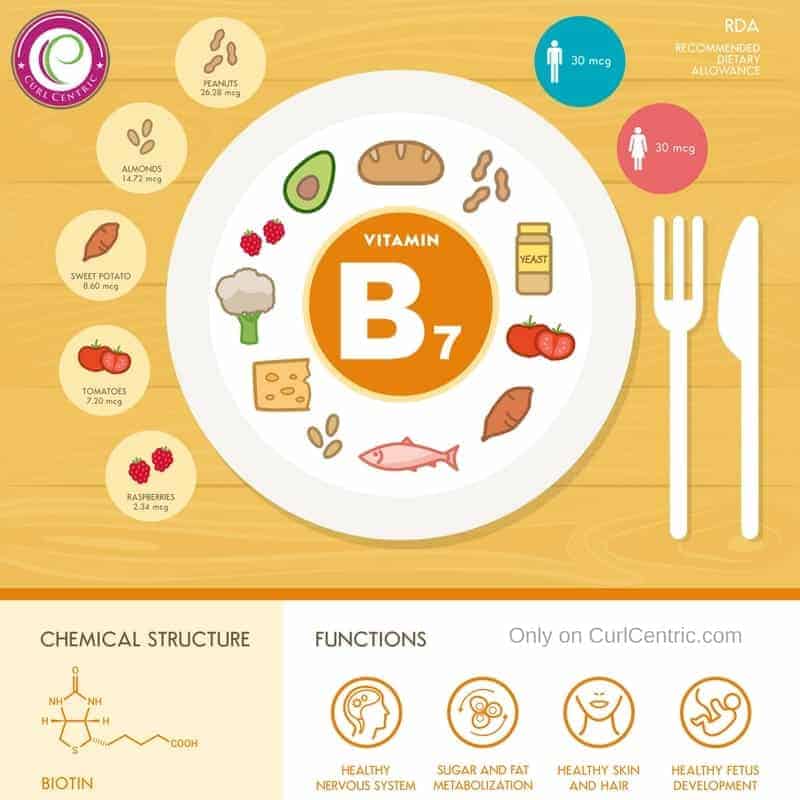
Sources: Food High in Vitamin B7
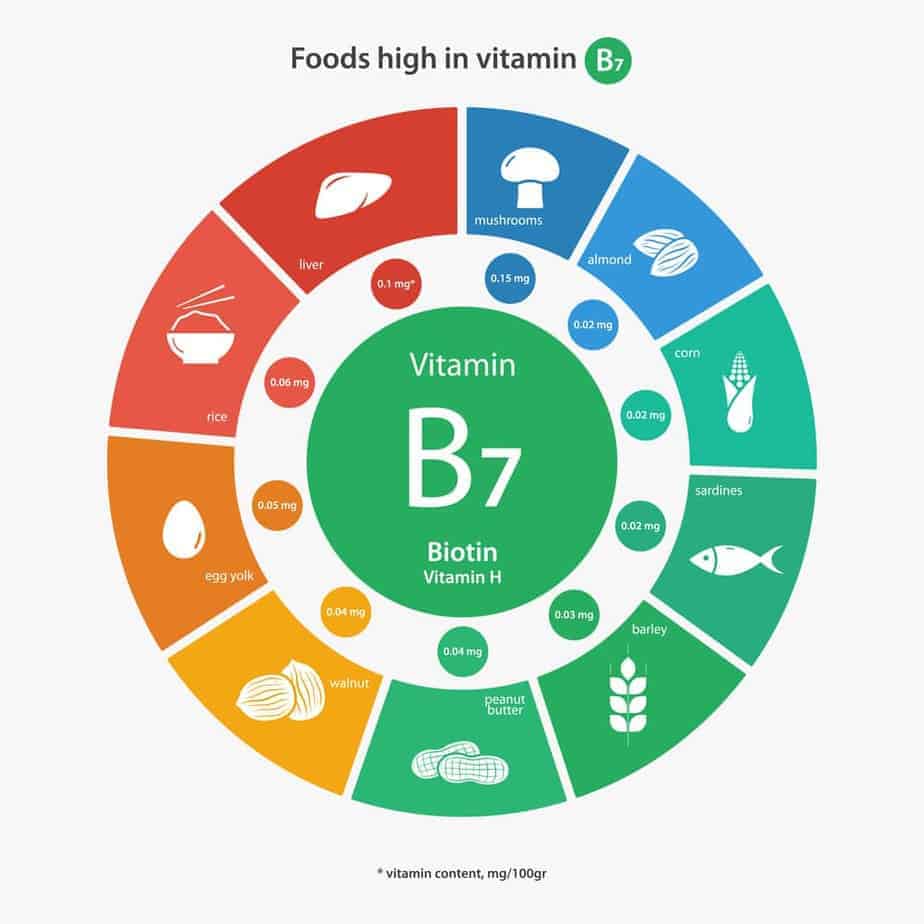
Using Biotin for Healthy Hair Growth: The Reason People Are Taking Biotin Supplements
Over the years, biotin supplements have been used to treat numerous conditions, but most naturals who take it have one common goal. There is a common belief that taking a biotin supplement will improve your ability to grow long hair.
Using vitamins for hair growth is common in the natural hair community. Biotin supplements are frequently recommended for faster hair growth (i.e., increasing the overall hair growth rate) and for strengthening nails - even though there's not sufficient scientific data to support its effectiveness.
According to clinical references, researchers haven’t come to an agreement on the benefits of taking additional biotin as an oral supplement. There is anecdotal evidence that suggests biotin may have additional benefits.
However, I have not found any supporting scientific evidence that verifies the perception that biotin improves hair growth potential. Nevertheless, biotin is commonly found in a variety of health and cosmetic products for skin and hair.
Did You Know That Biotin Deficiencies Are Very Rare?
Biotin deficiency is extremely rare, particularly due to the fact that it's available in a wide range of foods and that the human body needs very little biotin. The average person doesn’t need a biotin supplement.
You receive vitamin B7 naturally in everyday foods like whole-grain cereals, whole wheat bread, eggs, dairy products, salmon, and chicken. Note that this isn't a complete list of foods that provide vitamin B7.
Although, it's important to note that since our bodies can recycle vitamin B7 that the body already contains, genuine deficiencies of vitamin B7 are very rare.
If you believe you have a deficiency, we always recommend working with an appropriately licensed medical professional to create a personalized plan of treatment.
Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology
According to the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, people who have biotin deficiencies can increase hair growth back to the normal rate by consuming low biotin doses.
Regardless of the cause of the deficiency, it can usually be directly addressed by nutritional supplementation.
Examples of deficiency symptoms are:
- Conjunctivitis
- Hair loss ( alopecia)
- Thin and brittle fingernails
- Neurological symptoms such as lethargy, depression, tingling and numbness on the extremities, and hallucination
- Dermatitis (usually a scaly red rash around the nose, mouth, eyes, and genital area)
According to the European Journal of Paediatric Neurology, children who take certain anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) may suffer hair loss as a secondary effect. This hair loss might be treated with biotin supplementation. The medication may cause biotin deficiency, and supplementation improves hair back to normal levels.
How Much Vitamin B7 Should You Take?
The Food and Nutrition Board (i.e., The Institute of Medicine) provided updated Estimated Average Requirements (EARs) and Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA) for B vitamins in 1998.
At the time, they did not have enough information to establish RDAs and EARs for Vitamin B7. In such instances, the board often established Adequate Intakes (AIs), with the expectation that they will be replaced by RDAs and EARS at a later date.
The Institute of Medicine has set parameters defining an adequate intake of biotin. If you eat a healthy hair diet, you should receive an adequate amount of biotin naturally without requiring supplements.
If you decide to take biotin, the “appropriate” dose needed depends on many factors and should really be prescribed by a medical doctor.
Should You Worry About Toxicity with Vitamin B7?
Certain animal studies have indicated very few, if any, side effects of consuming high doses of vitamin B7.
These studies suggest that both humans and animals can tolerate doses at least one order of magnitude higher than the adequate intake recommended by the Institute of Medicine's Food and Nutrition Board.
Thus far we haven't been able to find any reports of significant adverse effects from high doses of vitamin B7. Outside of acne, even when vitamin B7 is used in high quantities, such as in the treatment of metabolic disorders that cause seborrheic dermatitis in children the side effects appear to be tolerable by most women.
Excess biotin accumulation may inhibit endogenous sirtuin activity, which leads to increased inflammation as well as collagen deposition and cellularity, and could be associated with age-related metabolic problems.
I’ve seen many women discuss taking very high levels of biotin. These high intake levels may prove to be safe eventually; however, researchers haven’t been able to determine if consuming high dosages of biotin over an extended period of time will pose health risks.
I encourage you to focus on your eating habits since you can get plenty of biotin by eating a healthy diet.
Although, if you decide to use supplements it appears (based on what we currently know) that there really isn't a significant risk to trying the supplements - meaning there may not be a significant health risk.
The Best Hair Vitamins (Other Than Biotin) for Faster Hair Growth

Regardless of whether we agree with the general sentiment, long healthy natural hair can be seen as a sign of beauty. Just think of all the natural hair idols online and the comments that you read under their photos.
With hair growth being a common desire of many women, let’s talk about hair growth vitamins other than biotin. There are numerous factors that must be considered when trying to encourage your hair to grow longer, including age, genetics, and hormones.
Click here if you want to read our advanced guide to hair growth, otherwise let’s discuss hair growth vitamins and supplements, other than biotin, that are supportive of hair growth.
Vitamin A
Within the body, all human cells including your hair need vitamin A.
An appropriate amount of vitamin A can help your skin make sebum, which is an oily substance to help keep your scalp moisturized and your hair healthy.
Deficiency in vitamin A can cause issues related to hair loss, but too much vitamin A can be just as detrimental. There are studies that have shown that too much vitamin A can lead to hair loss.
Many foods contain an abundance of beta-carotene, which is later turned into vitamin A within the body, including sweet potatoes, carrots, pumpkins, spinach, and kale. Yogurt, eggs, milk, and cod liver oil are also a good source of vitamin A.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C identifies as a powerful antioxidant that protects your hair against oxidative stress caused by free radicals. Free radicals have the ability to block hair growth and leave your hair with an aged appearance.
Vitamin C also assists with creating collagen which is an important aspect of the hair's structure.
Vitamin C assists the body with iron absorption, which is another mineral needed for hair growth. Within food, vitamin C can be found in strawberries, peppers, guavas, and citrus fruits.
Vitamin D
Deficiencies in vitamin D are directly linked to alopecia, which is the medical term for hair loss. According to this study, a sufficient supply of vitamin D may also help create new hair follicles, which are the pores where hair grows.
Many researchers believe that vitamin D plays a significant part in hair production, although most research has only focused on vitamin D receptors.
There is little known about how vitamin D assists with the hair growth process. Many people have vitamin D deficiencies, and it’s usually a good idea to increase your vitamin D levels.
Your body can produce vitamin D naturally through sun exposure, so spend some time outside enjoying the sun. Although, vitamin D can also be absorbed through foods such as fatty fish, cod liver oil, fortified foods, and some mushrooms.
It’s unknown exactly how vitamin D plays a role in hair growth, but a vitamin D deficiency can be directly linked to certain forms of hair loss.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E has similar characteristics to vitamin C as it prevents free radicals from harming the hair.
In one research study, whose population were those who experienced hair loss, there was a 34.5% increase in hair growth after taking vitamin E supplements for 8 months, compared to the placebo group within the study, which only had a .1% increase in hair growth.
Foods rich in vitamin E include sunflower seeds, almonds, spinach, and avocados.
Iron
Iron also has benefits for hair growth by assisting your red blood cells in carrying oxygen to cells. Women are prone to anemia when they are deficient in iron, which has a side effect of hair loss.
Foods with plenty of iron include clams, oysters, eggs, red meat, spinach, and lentils.
Zinc
Hair loss is also common in those who are zinc deficient, as zinc encourages hair tissue growth and repair. Studies have proven that when people take zinc supplements, their hair loss issues improve, however, there is anecdotal evidence that too much zinc can lead to hair loss issues (source).
To ensure that you don’t intake too much zinc, it’s best to get zinc from whole foods such as oysters, beef, spinach, wheat germ, pumpkin seeds, and lentils.
Protein
It is essential to consume an appropriate amount of protein, especially for hair health as hair is made from protein.
Studies have shown that those who do not consume enough protein will likely suffer from slower hair growth and potentially hair loss. However, for people that reside in Western countries protein deficiencies are extremely rare.
- How to Get Thick Hair With Coconut Oil
- How Long Does It Take for Hair to Grow 2 Inches
- How Often Should You Use Rice Water on Natural Hair
- When Is the Best Time to Take Biotin Vitamins?
Are Hair Growth Vitamins and Supplements Safe?
Most of the vitamins and minerals needed for healthier hair (and hair growth) can be found naturally in foods, however, those who receive enough vitamins from a balanced diet (like this yoga diet plan) may find hair growth supplements helpful.
Research has determined that those who are already deficient will find supplements most beneficial.
It is important to remember that, in some cases, too many vitamins and minerals can be just as harmful as not consuming enough.
We suggest speaking with your medical doctor or another appropriately licensed medical professional, before starting a regimen of hair growth vitamins or supplements. I’m not trying to scare you, but I do want you to be careful. Take care.




