Biotin is a popular supplement for women and men alike. Whether you plan on taking starting a biotin treatment for health or beauty reasons, you’re probably wondering what side effects you can expect.
One of the most commonly rumored side effects of the vitamin is headaches. Can biotin cause headaches?
So, in this article, we’ll take a look at whether there’s any truth to the rumor. We’ll also answer some of your other biotin-related questions, which will help you get all of the rewards with minimal (if any) side effects!
Table of Contents
Can Biotin Cause Headaches?
Unfortunately, biotin supplements can cause headaches. Although there is a shortage of research into the subject, early studies suggest a link between biotin supplements and migraines.
In a recent study involving 24,347 people, 1,772 experienced headaches shortly after starting a biotin regimen.
In addition to this study, biotin users have been sharing their experiences on beauty forums and social media websites. While headaches aren't the most commonly reported symptom, many users list them as a side effect.

Biotin, or b7, is an organic compound belonging to a group of B vitamins. B vitamins play a substantial role in energy metabolism and nervous system function.
They help transform macronutrients like carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into a form of energy that your body can actually use. While biotin is usually obtained through the foods you eat, some people take it as a supplement.
How Do You Prevent Biotin Headaches?
The bad news is that biotin can cause headaches. The good news is that you can take certain measures to lower your risk of experiencing them. Start by taking the lowest concentration possible.
The higher your dose, the more likely you are to experience headaches. You should also take your supplements with plenty of water. The water will help accelerate the movement of the B vitamin through your system.
Another way some users avoid biotin-induced headaches is by taking the supplement at night. However, this method might not work for everyone.
B vitamins, like biotin, can give you a mild energy boost after you take them. That can make falling asleep difficult for some people.
What Are the Other Side Effects of Biotin?
Taking small amounts of biotin each day is generally regarded as safe. However, many biotin supplements come in much larger doses than what’s needed daily. In addition to headaches, biotin supplements can cause a host of other side effects when taken in excess.
While most people can use it without issue, biotin supplements occasionally cause:
- Difficulty sleeping
- Skin rashes and acne
- Skewed blood tests (e.g., thyroid function tests, thyroid disease, etc.)
- Digestion issues
Is It Good to Take Biotin Every Day?
Biotin is a water-soluble vitamin, so it's considered safe to take daily. Unlike fat-soluble vitamins, water-soluble vitamins don’t get stored in your fat cells when you ingest too many.
Instead, the excess biotin simply passes through your urine. Because you don’t run the risk of developing toxicity, most people can take daily biotin supplements without issue.
However, only a healthcare provider offering professional medical advice can tell you whether it's safe for you to take biotin daily. Always check with a healthcare professional before starting a new biotin regimen.
Since most people get an adequate amount of biotin through their diet, the supplements are usually only recommended for people who are deficient. However, there’s no way of knowing if you’re deficient without speaking with a medical professional.
Your doctor can perform blood work to determine where your biotin levels fall. Then, they may or may not recommend biotin supplements to bring your levels into a healthy range.
How Do You Know if You Are Taking Too Much Biotin?
Because biotin is water soluble, most people won’t face adverse effects from taking too much. Despite this, biotin toxicity is still possible. Signs of a biotin overdose include insomnia, frequent urination, and excessive thirst.
As soon as you start experiencing these symptoms, either cut back on your biotin consumption or stop using it entirely. If the symptoms persist, reach out to a medical professional right away.
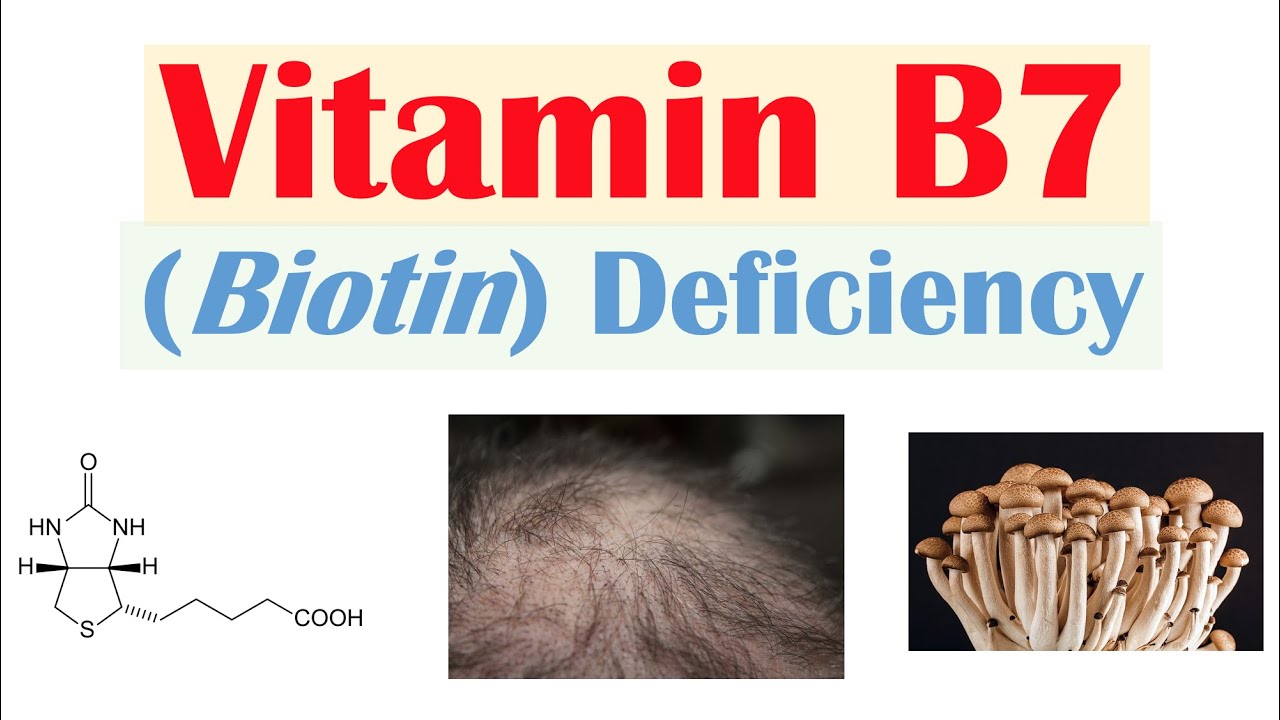
What Are the Signs of a Biotin Deficiency?
Although biotin deficiency (i.e., biotinidase deficiency) is rare in healthy adults, it can arise due to an extremely limited diet, changes in gut bacteria, and certain medications. Signs of a biotin deficiency include:
- Thinning hair and hair loss
- Brittle nails
- Skin rashes or infections
- Seizures
- Neurological issues like lethargy, depression, and hallucinations.
Also, as we mentioned earlier, the people who will benefit most from taking biotin are those with a deficiency. Unlike other vitamins, your body isn’t able to produce biotin naturally. Instead, the bacteria living in your gut synthesize it from the foods you eat.
Does Biotin Help Your Hair Grow?
One of the main reasons why people take biotin is because they’ve heard it can improve their hair’s growth rate and thickness. This is because biotin stimulates keratin, the protein that your hair is made of.
While there isn’t any conclusive evidence that biotin makes your hair grow faster or fuller, there is plenty of anecdotal evidence suggesting it does. Many users report fuller, longer locks within the first few months of taking biotin regularly.
If you have a biotin deficiency, you may start to see an improvement in your hair, skin, and nails much more quickly. In cases involving a biotin deficiency, users see results in as few as one to two months!

How Much Biotin Should You Take for Hair Growth?
While the link between biotin and faster hair growth is largely unstudied, taking biotin supplements may increase your hair growth rate. Most healthy adults only need around 30 to 60 micrograms of biotin each day.
However, most biotin supplements contain significantly more. As with other vitamins and supplements, you want to take the minimum necessary amount.
We recommend consulting a doctor to determine how much biotin you should take daily.
You may require more or less biotin than the average person if one or more of the following apply to you:
- You’re a smoker (smoking accelerates biotin catabolism)
- You’re pregnant or breastfeeding
- You have digestive or intestinal problems
- You’re on certain medications (e.g., chromium picolinate)
- You eat raw egg whites
What Foods Are High in Biotin?
One way to avoid the potential risks of taking biotin supplements is to eat more biotin-rich foods. There are a variety of foods that contain naturally high levels of biotin.
Additionally, vitamin-rich foods tend to be more healthy and beneficial than taking supplements. You also don’t need any expensive or potentially painful bloodwork!
Simply make more of an effort to incorporate the following foods into your diet.
- Cooked eggs - Raw egg whites can actually lead to a biotin deficiency, so make sure your eggs are fully cooked before you consume them.
- Seeds and nuts - Some of the most biotin-rich seeds and nuts include walnuts, almonds, sunflower seeds, peanuts, and pecans.
- Vegetables - Certain vegetables, like spinach, mushrooms, sweet potato, and broccoli, contain high levels of biotin.
- Milk - Dairy products, like milk, cheese, and yogurt, are an excellent source of biotin.
- Organ meats - Although not everyone eats them, organ meats are some of the richest sources of biotin available.
- Fruits - While most fruits don’t have significant amounts of biotin, bananas, raspberries, and avocados are exceptionally high in the vitamin.
Unfortunately, headaches are regularly listed as a side effect of taking biotin supplements. But luckily, the vast majority of people who try them won’t have to deal with any unwanted symptoms.
If you do experience headaches, try reducing the amount of biotin you take, and make sure you’re drinking plenty of water. And with that, we hope we’ve answered all of your questions today!